Scatter plots and data quick check, indispensable tools in the realm of data analysis, unveil hidden patterns, trends, and outliers, empowering analysts to make informed decisions and draw meaningful conclusions from complex datasets.
Scatter plots, graphical representations of the relationship between two variables, provide a visual depiction of data, enabling analysts to identify correlations, clusters, and potential relationships between variables. Data quick checks, on the other hand, offer a rapid assessment of data quality, ensuring its accuracy and completeness, and laying the groundwork for reliable analysis.
Scatter Plots: Scatter Plots And Data Quick Check
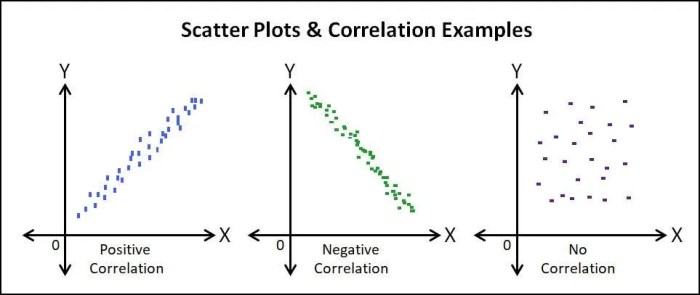
Scatter plots are graphical representations of data that show the relationship between two numerical variables. Each data point is plotted as a dot on a two-dimensional plane, with the horizontal axis representing one variable and the vertical axis representing the other.
Scatter plots can be used to identify patterns, trends, and outliers in data. They can also be used to make predictions about future values of one variable based on the values of another variable.
Types of Scatter Plots
- Positive correlation:The points in a scatter plot show a positive correlation if they form a line that slopes upward from left to right.
- Negative correlation:The points in a scatter plot show a negative correlation if they form a line that slopes downward from left to right.
- No correlation:The points in a scatter plot show no correlation if they are randomly scattered.
Purpose and Benefits of Scatter Plots
- Identify patterns and trends in data
- Make predictions about future values of one variable based on the values of another variable
- Identify outliers in data
- Communicate data in a visually appealing way
- Check for missing values:Examine the data to identify any missing values. Missing values can be a sign of data entry errors or other problems.
- Check for outliers:Outliers are data points that are significantly different from the rest of the data. Outliers can be caused by data entry errors or other problems.
- Check for data types:Ensure that the data is in the correct data type. For example, dates should be in a date format, and numbers should be in a numeric format.
- Check for consistency:Check that the data is consistent within itself. For example, if the data includes customer ages, ensure that the ages are all positive.
- Customer segmentation:Scatter plots can be used to segment customers based on their age and spending habits.
- Product development:Scatter plots can be used to identify the relationship between product features and customer satisfaction.
- Financial analysis:Scatter plots can be used to identify the relationship between stock prices and economic indicators.
Data Quick Check

A data quick check is a preliminary examination of data to identify errors, inconsistencies, and missing values. It is an important step in data analysis, as it helps to ensure that the data is accurate and reliable.
Steps Involved in Performing a Data Quick Check
Importance of Data Quick Check
Data quick checks are important because they help to ensure that the data is accurate and reliable. This is important for data analysis, as inaccurate or unreliable data can lead to misleading results.
Scatter Plots and Data Quick Check in Practice
Scatter plots can be used as a tool for performing data quick checks. By plotting the data on a scatter plot, it is easy to identify patterns, trends, and outliers in the data.
For example, a scatter plot of customer age versus customer spending might show a positive correlation, indicating that older customers tend to spend more money. This information could be used to target marketing campaigns to older customers.
Limitations of Scatter Plots
Scatter plots are a useful tool for data quick checks, but they have some limitations. For example, scatter plots can be difficult to interpret if the data is clustered or if there are many outliers.
Additionally, scatter plots can only show the relationship between two variables. If there are more than two variables that are related, a scatter plot may not be the best way to visualize the data.
Advanced Applications of Scatter Plots
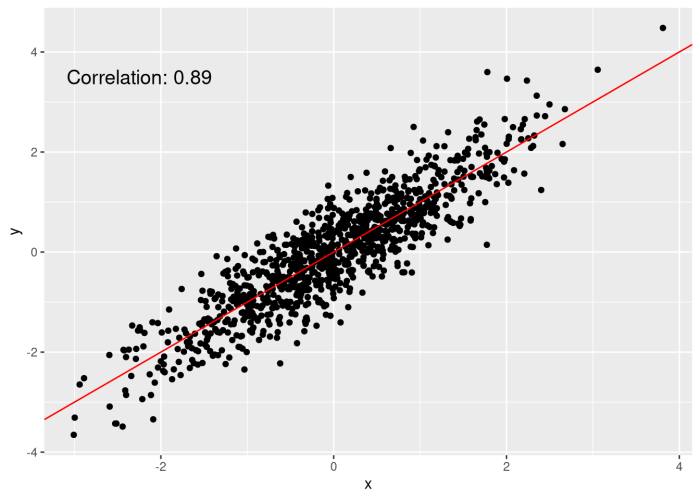
Scatter plots can be used for more than just data quick checks. They can also be used for advanced data analysis, such as regression analysis and hypothesis testing.
Regression Analysis, Scatter plots and data quick check
Regression analysis is a statistical technique that uses scatter plots to determine the relationship between two or more variables. Regression analysis can be used to make predictions about future values of one variable based on the values of another variable.
Hypothesis Testing
Hypothesis testing is a statistical technique that uses scatter plots to test whether there is a significant difference between two groups of data. Hypothesis testing can be used to determine whether there is a relationship between two variables.
Machine Learning and Data Visualization
Scatter plots are also used in machine learning and data visualization. In machine learning, scatter plots can be used to visualize the data that is being used to train a model. In data visualization, scatter plots can be used to create interactive visualizations that allow users to explore data in a variety of ways.
Examples and Case Studies
Scatter plots are used in a variety of real-world applications. Here are a few examples:
FAQ Explained
What is the purpose of a scatter plot?
Scatter plots visualize the relationship between two variables, allowing analysts to identify correlations, clusters, and potential relationships.
How does a data quick check help in data analysis?
Data quick checks ensure data quality and completeness, providing a solid foundation for reliable analysis.
What are the limitations of scatter plots?
Scatter plots can be misleading if the data contains outliers or if the relationship between variables is non-linear.