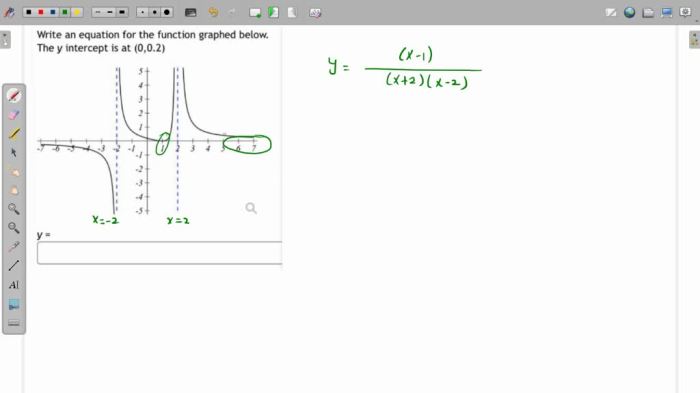
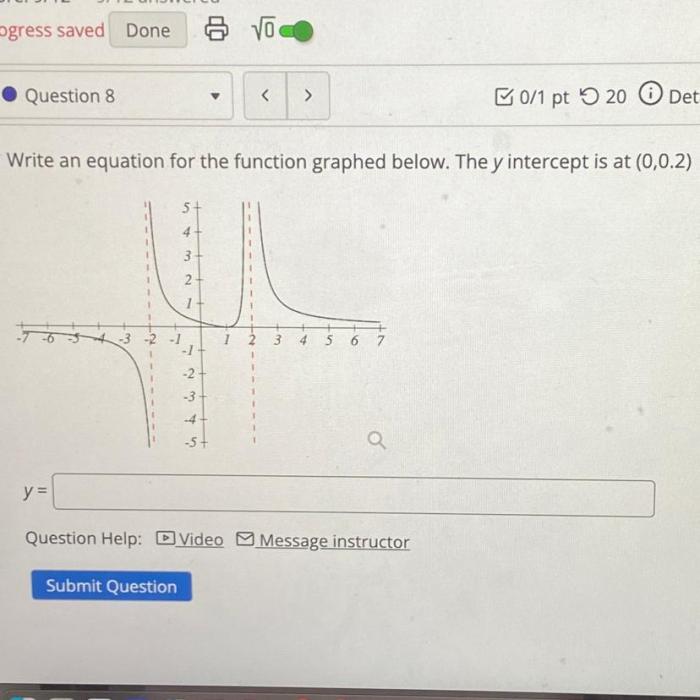
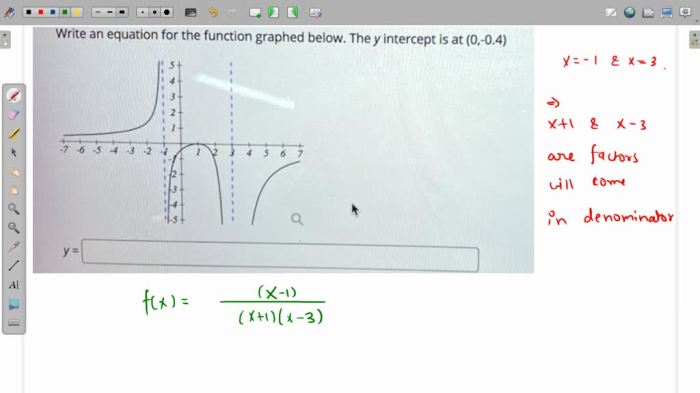
Write the equation for the function graphed below. This question often arises in various mathematical contexts, prompting us to delve into the fascinating world of graph analysis and equation derivation. This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and skills to tackle this challenge with confidence, empowering you to uncover the hidden mathematical relationships within any given graph.
Throughout this journey, we will explore the fundamental concepts of graph analysis, including identifying key features, understanding different types of equations, and applying effective methods for equation derivation. We will also examine various representation methods, enabling you to express the equation of a graph in multiple formats.
By the end of this guide, you will possess a deep understanding of the intricate connection between graphs and equations, empowering you to solve complex problems and make informed decisions.
Equation Identification: Write The Equation For The Function Graphed Below.
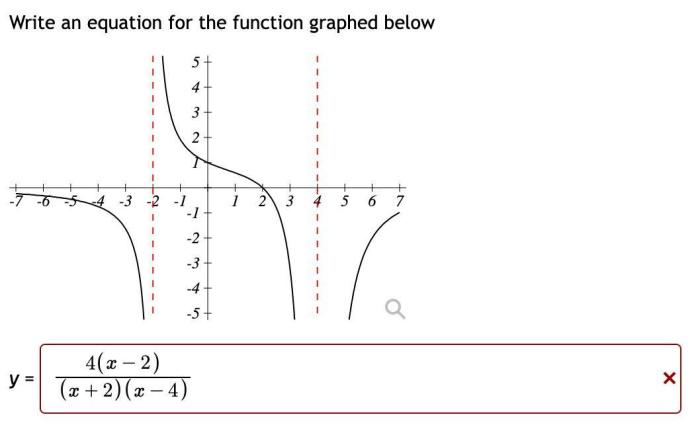
Identifying the equation for a given graph involves understanding the relationship between the graph’s shape and its mathematical representation. Different types of graphs correspond to specific equations, such as linear graphs (straight lines) represented by linear equations, quadratic graphs (parabolas) represented by quadratic equations, exponential graphs (curves that increase or decrease rapidly) represented by exponential equations, and logarithmic graphs (curves that increase or decrease slowly) represented by logarithmic equations.
Graph Analysis
To analyze a graph and determine its equation, it’s crucial to identify key features such as intercepts (where the graph crosses the x- and y-axes), slopes (the steepness of the graph), and asymptotes (lines that the graph approaches but never touches).
By examining these features, it’s possible to narrow down the potential equations that could represent the graph.
Equation Derivation, Write the equation for the function graphed below.
Deriving the equation of a graph involves using the key features identified during graph analysis. For linear graphs, the slope-intercept form (y = mx + b) is commonly used, where ‘m’ represents the slope and ‘b’ represents the y-intercept. Quadratic graphs can be represented using the standard form (y = ax² + bx + c), where ‘a’, ‘b’, and ‘c’ are constants.
Exponential and logarithmic graphs require more advanced techniques, such as the use of logarithms or exponential functions.
Equation Representation
The equation of a graph can be represented in various forms, each with its own advantages. The slope-intercept form is useful for visualizing the graph’s slope and y-intercept. The point-slope form (y – y1 = m(x – x1)) is useful when a specific point on the graph is known.
The standard form is often used for more complex equations, such as quadratic equations.
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the significance of identifying the equation of a graph?
Identifying the equation of a graph is crucial because it allows us to understand the mathematical relationship represented by the graph. The equation provides a concise and precise description of the function’s behavior, enabling us to make predictions, perform calculations, and solve problems related to the graph.
How can I determine the equation of a graph if I don’t know its type?
If you are unsure about the type of graph, start by analyzing its key features, such as intercepts, slopes, and asymptotes. These features can provide valuable clues about the potential equation. You can then use methods like point-slope form or the slope-intercept form to derive the equation.
What are the advantages of using different equation representation methods?
Different equation representation methods offer advantages in specific situations. Slope-intercept form is convenient for finding the slope and y-intercept of a line. Point-slope form is useful when you know a point on the graph and the slope. Standard form is commonly used for polynomial equations and conic sections.