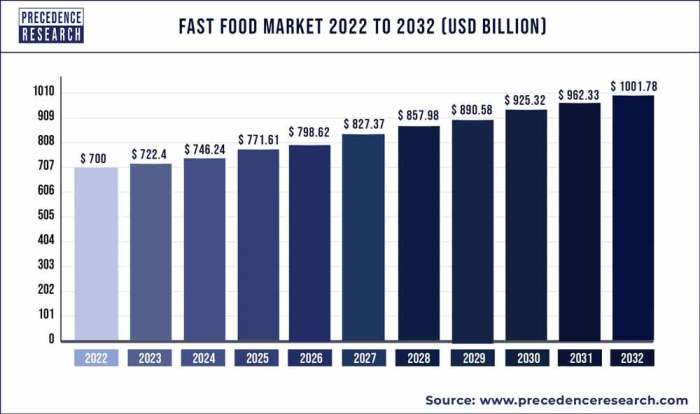
Which industry would be best characterized as monopolistically competitive? This intriguing inquiry sets the stage for an illuminating exploration into a market structure where firms wield limited market power amidst a landscape of differentiated products.
Monopolistic competition, a fascinating blend of perfect competition and monopoly, presents a unique market environment where numerous firms compete while possessing some degree of market control. This intricate interplay between competition and differentiation gives rise to distinctive industry dynamics, pricing strategies, and welfare implications.
Monopolistic Competition: Which Industry Would Be Best Characterized As Monopolistically Competitive
Monopolistic competition is a market structure in which many firms sell differentiated products that are close substitutes for one another. Each firm has some market power because of the uniqueness of its product, but no firm has a dominant share of the market.
Monopolistic competition is characterized by the following features:
- Many firms: There are many firms in the market, so no single firm has a dominant share.
- Differentiated products: The products sold by different firms are differentiated, meaning that they are not perfect substitutes for one another.
- Free entry and exit: Firms are free to enter or exit the market, so the number of firms in the market can change over time.
Pricing and Output
In monopolistic competition, firms set prices and output to maximize profits. The price that a firm sets depends on the demand for its product and the costs of production. The output that a firm produces depends on the price that it sets and the costs of production.
Product differentiation affects pricing and output in monopolistic competition. Because products are differentiated, firms have some market power. This market power allows firms to set prices above marginal cost. The amount of market power that a firm has depends on the degree of product differentiation.
Entry and Exit
Firms are free to enter or exit the market in monopolistic competition. This means that the number of firms in the market can change over time. Firms will enter the market if they expect to make a profit, and they will exit the market if they expect to lose money.
Entry and exit affect the long-run equilibrium of monopolistic competition. In the long run, the number of firms in the market will adjust until the profits of all firms are zero.
Welfare Implications, Which industry would be best characterized as monopolistically competitive
Monopolistic competition has several welfare implications. First, it leads to product variety. Because firms in monopolistic competition produce differentiated products, consumers have a wide range of choices. Second, it leads to lower prices than would be possible in a monopoly.
However, monopolistic competition also has some negative welfare implications. First, it can lead to excess capacity. Because firms in monopolistic competition produce differentiated products, they often have excess capacity. This excess capacity can lead to higher costs and lower profits for firms.
Helpful Answers
What are the key characteristics of monopolistic competition?
Monopolistic competition is defined by numerous firms, differentiated products, easy market entry and exit, and limited market power.
How do firms in monopolistic competition determine pricing?
Firms consider both the demand for their differentiated products and the pricing decisions of competitors when setting prices.
What are the welfare implications of monopolistic competition?
Monopolistic competition generally leads to consumer welfare gains compared to monopoly but may result in inefficiencies relative to perfect competition.